OLED(Organic Light Emitting Diode)
OLED displays utilize organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied. It is thin, lightweight, and offers flexibility in display implementation, making it suitable for flexible and transparent displays, as well as for automotive displays and AR/VR applications.
-
1st Generation
Fluorescent Material-
1963
First organic luminescence in Antracene crystal
-
1987
Formation of low-molecular-weigh organic thin-film structures with Alq3, TPD -> First practical OLED
-
1989
Host(Alq3) - Dopant(DCM) system emerge
-
1990
PPV
Discovery of EL properties in conjugated polymers
-
-
2nd Generation
Phosphorescent Material-
1998
Development of phosphorescent dopant based on organometallic compounds such as PT(OEP), Ir(PPy), etc.
-
-
3rd Generation
Natural Fluorescent Material-
2010
TADF(Thermal Activated Delayed Fluoresence) device development
-
-
4th Generation
Luminescent Material-
2010's
Hyper Fluorescence device development and research in progress
-
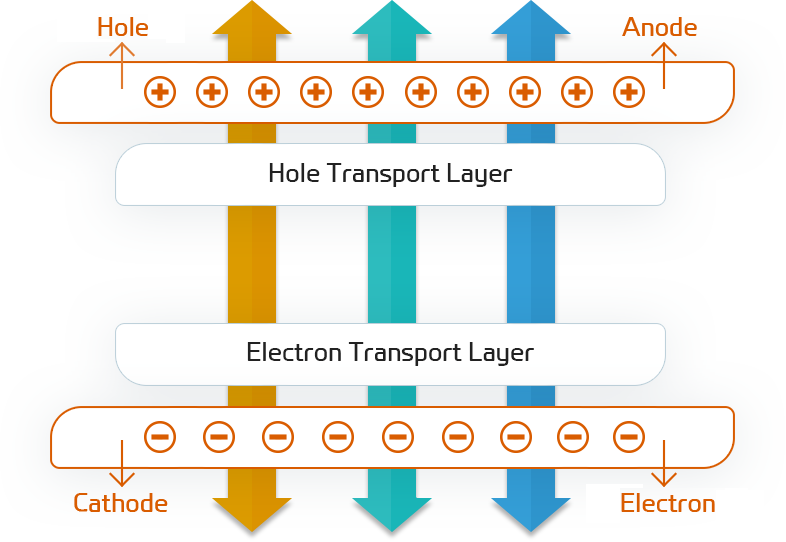
OLED Structure
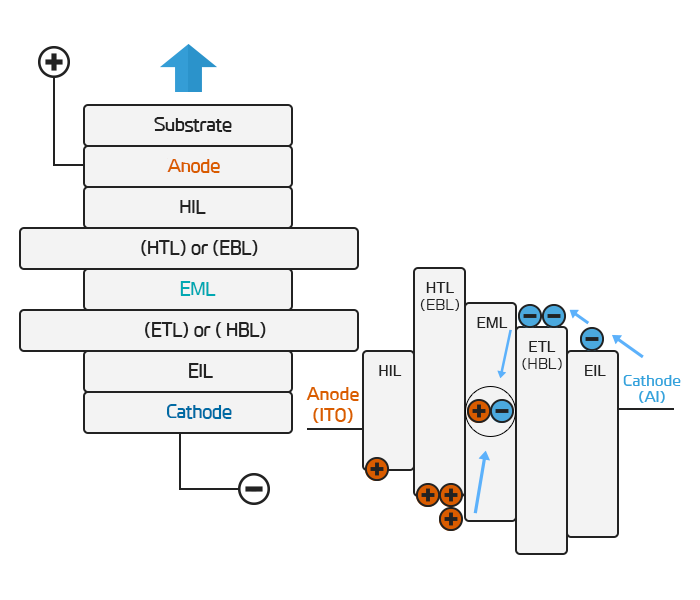
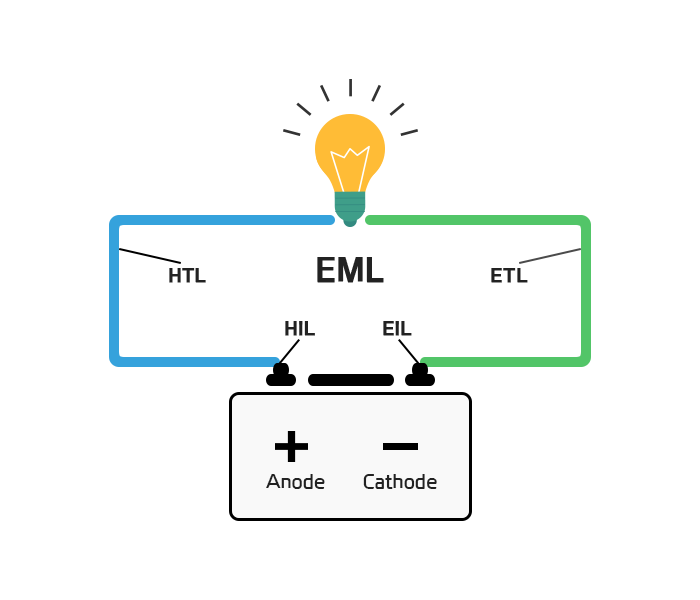
| Cathode | Acts as a reflective layer to inject electrons |
|---|---|
| EIL(Electron Iniection Layer) | A layer that injects electrons generated from Cathode |
| ETL(Electron Transfer Layer) | Electron transport layer |
| EML(Emission Layer) | Luminescent layer |
| HTL(Hole Transfer Layer) | Electron holes transport layer |
| HIL(Hole Injection Layer) | Electron holes injection layer |
| Anode | Role of injecting electron holes |
Next generation OLED – Transparent OLED Structure
OLED Product
| HIL | HI - 011 / 012 / 013 | |
|---|---|---|
| HTL | HT - 001 / 012 / 013 / 014 / 015 / 017 | |
| EML (fluorescence) |
Q-03-001 | BH - 011 / 012. RH - 011 |
| Q-03-002 | BD - 011 | |
| EML (phosphorescene) |
Q-03-004 | HT - 016 |
| Q-03-005 | GD - 011. RD - 011 | |
| ETL | ET - 011 / 012 | |
| EIL | ET - 011(Liq) | |
| Intermediate | ON - 201 / 202 / 203 / 204 / 301 / 302 / 303 /306 /308 | |
Customer response
-
1
Customer request
-
2
Technical consulting
-
3
Request sample production
-
4
Approval/contract, Subsidiary materials supply
-
5
Pilot production
-
6
Mass production/Delivery